Web Hosting Services: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
Web hosting is a crucial service that enables individuals and organizations to publish their websites on the internet. It involves providing the infrastructure, technologies, and services necessary for storing and serving website content. This guide aims to delve deep into web hosting services, exploring their types, features, benefits, and considerations for choosing the right hosting provider.
1. Understanding Web Hosting
1.1 What is Web Hosting?
At its core, web hosting involves renting server space where websites can store their files, databases, and content. When a user types a website’s URL into their browser, a request is sent to the hosting server, which then delivers the requested content to the user.
1.2 How Web Hosting Works
- Domain Name System (DNS): When you enter a domain name, DNS translates it into an IP address that points to the hosting server.
- Server Response: The server processes the request, retrieving the necessary files (HTML, CSS, images) and sending them back to the user’s browser.
- Display: The browser then renders the webpage for the user to view.
2. Types of Web Hosting
2.1 Shared Hosting
In shared hosting, multiple websites share the same server resources. This is a cost-effective solution suitable for small businesses or personal blogs.
Pros:
- Affordable pricing.
- Easy to set up.
- Maintenance handled by the host.
Cons:
- Limited resources.
- Performance can be affected by other sites on the server.
2.2 VPS Hosting (Virtual Private Server)
VPS hosting provides a virtualized server environment, offering more control and dedicated resources compared to shared hosting.
Pros:
- More resources than shared hosting.
- Greater customization options.
- Better performance.
Cons:
- More expensive than shared hosting.
- Requires some technical knowledge.
2.3 Dedicated Hosting
Dedicated hosting provides an entire server for a single user, offering maximum control, performance, and security.
Pros:
- Complete control over server settings.
- High performance and reliability.
- Enhanced security features.
Cons:
- High cost.
- Requires technical expertise for management.
2.4 Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting utilizes a network of servers to host websites, allowing for scalability and flexibility. It distributes resources across multiple servers, enhancing reliability.
Pros:
- Scalable resources.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing.
- High uptime and redundancy.
Cons:
- Can become expensive with high traffic.
- Complexity in managing resources.
2.5 Managed WordPress Hosting

This type of hosting is tailored specifically for WordPress sites. It includes optimized server configurations, automatic updates, and enhanced security features.
Pros:
- Optimized for WordPress performance.
- Automatic backups and updates.
- Enhanced security.
Cons:
- Generally more expensive than regular shared hosting.
- Limited to WordPress websites.
3. Key Features of Web Hosting Services
When selecting a web hosting provider, consider the following features:
3.1 Storage and Bandwidth
- Storage: Refers to the amount of disk space available for your website files.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data that can be transferred to and from your site, impacting how many visitors you can support.
3.2 Uptime Guarantee
Most providers offer an uptime guarantee, typically around 99.9%, ensuring that your website is accessible most of the time.
3.3 Security Features
Look for features such as SSL certificates, DDoS protection, firewalls, and regular backups to protect your website from threats.
3.4 Customer Support
Reliable customer support is essential, especially if you encounter technical issues. Look for 24/7 support via multiple channels (live chat, phone, email).
3.5 Control Panel
A user-friendly control panel (like cPanel) allows you to manage your hosting account, domains, and website files easily.
3.6 Scalability
Ensure that the hosting provider can accommodate your growth, allowing you to upgrade resources or migrate to a more powerful plan easily.
4. Benefits of Using Web Hosting Services
4.1 Professionalism
Having a dedicated web hosting service lends credibility and professionalism to your online presence.
4.2 Enhanced Performance
Hosting services optimize website speed and performance, ensuring faster load times and a better user experience.
4.3 Technical Support
Most hosting providers offer technical support, which is invaluable for troubleshooting issues that arise.
4.4 Data Security
Web hosting companies often provide security features that protect your website and data from cyber threats.
4.5 SEO Benefits
A reliable hosting service can improve your website’s SEO ranking due to better uptime and faster loading speeds.
5. Considerations When Choosing a Hosting Provider
5.1 Assess Your Needs
Identify your website’s requirements, such as expected traffic, content type, and necessary features.
5.2 Compare Pricing
Consider the total cost, including renewal rates, add-ons, and hidden fees.
5.3 Research Reputation
Read reviews and testimonials to gauge the reliability and quality of service of potential providers.
5.4 Evaluate Features
Ensure the hosting package includes essential features that align with your needs.
5.5 Check for Money-Back Guarantees
A money-back guarantee can provide peace of mind, allowing you to test the service without risk.
6. Popular Web Hosting Providers
6.1 Bluehost
Bluehost is known for its excellent customer support and is recommended by WordPress.org. It offers a range of hosting services suitable for beginners.
6.2 SiteGround
SiteGround is praised for its superior performance and customer service. It offers managed WordPress hosting with excellent uptime and security features.
6.3 HostGator
HostGator provides affordable shared hosting options and a user-friendly interface, making it ideal for small businesses.
6.4 A2 Hosting
A2 Hosting is recognized for its speed and performance optimization, catering to users seeking high-speed hosting solutions.
6.5 DreamHost
DreamHost offers a range of hosting plans with a focus on flexibility and reliability. It also emphasizes renewable energy in its operations.
7. Conclusion
Web hosting services are fundamental to establishing and maintaining an online presence. By understanding the types of hosting, key features, benefits, and considerations, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions when selecting a hosting provider. With the right hosting solution, you can ensure that your website is reliable, secure, and poised for success.
8. FAQs About Web Hosting
8.1 What is the difference between shared and dedicated hosting?
Shared hosting means multiple websites share the same server, while dedicated hosting provides an entire server for a single website, offering more resources and control.
8.2 Can I switch hosting providers later?
Yes, most hosting providers allow you to transfer your website to another host, though it may require some technical steps.
8.3 Do I need technical skills to use web hosting?
While some hosting types (like managed hosting) are user-friendly, basic knowledge of web technologies can be beneficial.
8.4 What is an SSL certificate, and do I need one?
An SSL certificate encrypts data transmitted between your website and users, enhancing security. It’s recommended for all websites, especially those handling sensitive information.
8.5 How can I improve my website’s performance?
Consider optimizing images, using caching solutions, selecting a reliable hosting provider, and minimizing unnecessary plugins.
9. Advanced Topics in Web Hosting
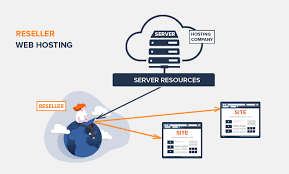
9.1 Reseller Hosting
Reseller hosting allows individuals or companies to purchase hosting services in bulk and resell them to their clients. This is an excellent option for web developers or agencies looking to offer hosting as part of their service package.
Key Features:
- Custom branding and billing.
- Full control over the hosting environment for clients.
- Potential for additional revenue streams.
9.2 Colocation Hosting
Colocation involves renting space in a data center to house your server hardware. Unlike traditional hosting, you own the physical server but rely on the data center for power, cooling, and internet connectivity.
Advantages:
- Complete control over your hardware and software.
- Enhanced security features provided by the data center.
- Reliable power and cooling systems.
9.3 Edge Hosting
Edge hosting brings content closer to users by using a network of servers distributed across various geographic locations. This reduces latency and speeds up content delivery.
Benefits:
- Improved load times for global users.
- Enhanced performance for dynamic websites.
- Better handling of spikes in traffic.
9.4 Managed vs. Unmanaged Hosting
In managed hosting, the provider takes care of server maintenance, security updates, and technical support. Unmanaged hosting requires you to handle these aspects yourself.
Considerations:
- Managed hosting is ideal for those who prefer a hands-off approach.
- Unmanaged hosting offers more flexibility and control for tech-savvy users.
10. Emerging Trends in Web Hosting
10.1 Green Hosting
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, many hosting providers are adopting eco-friendly practices. This includes using renewable energy sources and optimizing data centers for energy efficiency.
Key Providers:
- GreenGeeks
- A2 Hosting (offers carbon-neutral hosting)
10.2 AI and Automation in Hosting

Artificial intelligence is transforming the hosting landscape by automating tasks such as customer support, server monitoring, and performance optimization. This leads to more efficient operations and improved user experiences.
10.3 Serverless Hosting
Serverless hosting allows developers to build and run applications without managing server infrastructure. This model focuses on execution rather than provisioning servers, providing flexibility and scalability.
Key Features:
- Automatic scaling based on demand.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing.
- Simplified deployment processes.
11. Best Practices for Choosing a Web Hosting Provider
11.1 Define Your Needs
Before selecting a hosting provider, outline your specific requirements:
- Website type (blog, e-commerce, portfolio).
- Expected traffic and growth potential.
- Required features (e.g., email, databases, security).
11.2 Look for Reviews and Comparisons
Research customer reviews and expert comparisons to gauge the reputation of different providers. Consider factors like uptime, support quality, and user satisfaction.
11.3 Test Customer Support
Reach out to customer support with questions before making a decision. This will give you insight into their responsiveness and expertise.
11.4 Evaluate Terms and Conditions
Carefully read the terms of service, including policies on uptime guarantees, data ownership, and cancellation fees.
11.5 Plan for Scalability
Choose a hosting provider that can accommodate your future growth, allowing you to upgrade your plan or resources without hassle.
12. Comparing Popular Web Hosting Services
12.1 Bluehost vs. SiteGround
- Bluehost: Known for beginner-friendly options, robust customer support, and integration with WordPress.
- SiteGround: Offers excellent performance, superior customer support, and advanced security features, but at a higher price point.
12.2 A2 Hosting vs. HostGator
- A2 Hosting: Focuses on speed and performance, providing turbo servers for enhanced load times.
- HostGator: Offers affordable pricing and various plans, but may lack some of the performance optimizations of A2 Hosting.
12.3 DreamHost vs. GreenGeeks
- DreamHost: Renowned for its commitment to privacy, unlimited bandwidth, and a strong focus on WordPress hosting.
- GreenGeeks: Stands out for its eco-friendly hosting options and strong performance, appealing to environmentally conscious users.
13. Conclusion
Web hosting services play a pivotal role in establishing a successful online presence. By understanding the various types of hosting, key features, and emerging trends, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions that align with their goals. Whether you are launching a personal blog or a large e-commerce site, choosing the right hosting provider is essential for long-term success.
14. FAQs About Web Hosting (Continued)
14.1 How do I migrate my website to a new hosting provider?
Most providers offer migration services, or you can manually transfer files and databases. Backup your site before starting the migration process to avoid data loss.
14.2 What is the importance of an SSL certificate?
An SSL certificate encrypts data, ensuring secure connections between your website and users. It’s essential for protecting sensitive information and improving search engine rankings.
14.3 Can I host multiple websites on one account?
Yes, many hosting providers offer plans that allow you to host multiple domains under a single account, especially with VPS or dedicated hosting.
14.4 What should I do if my website goes down?
Contact your hosting provider’s support immediately to diagnose the issue. Regular backups can help restore your site quickly if necessary.
14.5 Is it possible to switch hosting providers without losing my data?
Yes, with proper planning and execution, including backing up your filesand databases, you can switch providers without losing data.

